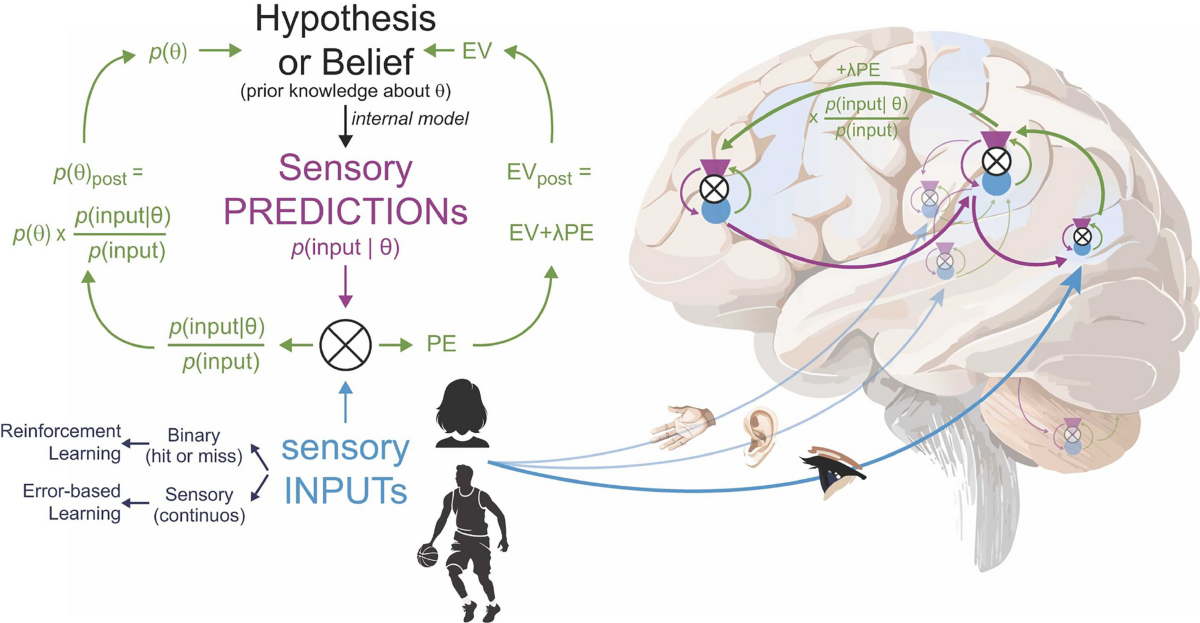
The Bayesian Brain is a neuroscience theory suggesting the brain acts as a prediction machine, using Bayesian Inference to constantly update internal probabilistic models of the world by balancing prior knowledge with incoming sensory evidence. It minimizes “prediction errors” (differences between what it expects and what it senses) to learn and adapt, explaining perception, action, and even phenomena like placebo as optimal statistical processing under uncertainty.
It stems from the Free Energy Principle and applications like Active Inference, but also shares a similar view to control theory applications of Bayesian Filtering like the Kalman Filter, similar to frameworks like Predictive Coding