Continuing from last lecture:
What about stability of period k points in R2?
For a=0.43,b=0.4, there is a period-2 orbit given by:
{(0.7,−0.1),(−0.1,0.7)}
To check stability, we could compute the Jacobian of f2 or multiply Jacobians of f at both points:
Df2(x)Df2((0.7,−0.1))=Df(f(x))⋅Df2(x)=Df((−0.1,0.7))⋅Df((0.7,−0.1))=eigenvalues ≈0.26±0.3i[0.12−1.40.080.4]
This implies that the period-2 orbit is a sink.
Stable and Unstable Manifolds
Lets consider the linear map f(x,y)=(22x,y):
orA=[20021]
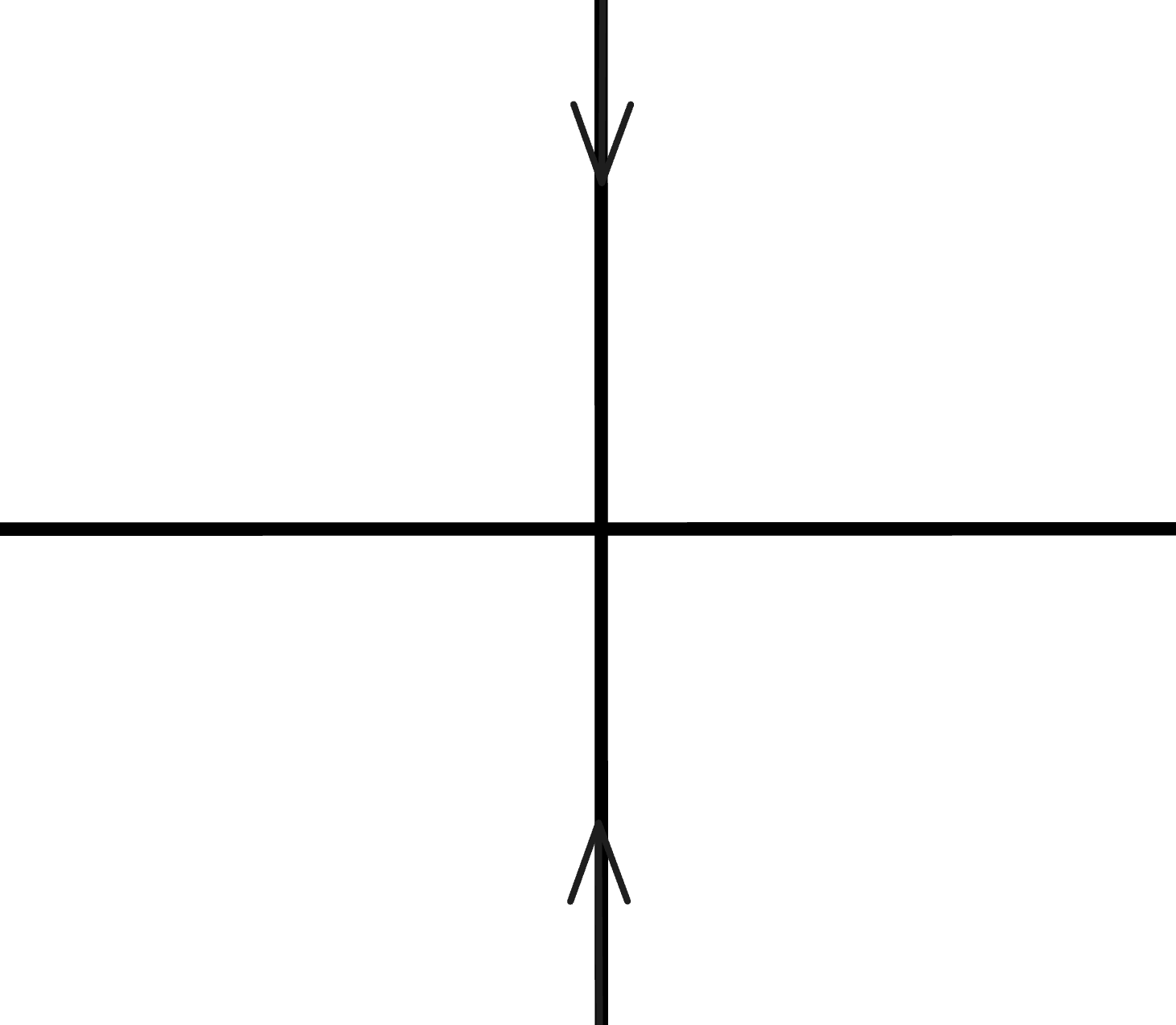
Points on the y-axis see origin as a sink. But we know it is a saddle. λ1=2,λ2=21,v1=[10],v2=[01]
source code
The y-axis is a Stable Manifold
The x-axis is a Unstable Manifold
We say a map f on Rm is one-to-one if:
f(v1)=f(v2)⇒v1=v2
If a function is one-to-one, then its inverse map is also a function f−1, e.g.:
f−1(x,y)=(y,2x)
Let f be a smooth 1-1 map on R2 and let p be a Saddle fixed point (or periodic saddle point)…
The Stable Manifold of p, call it S(p), is the set of points v such that:
∣fn(v)−fn(p)∣→0as n→∞
The Unstable Manifold of p, call it U(p), is the set of points v such that
∣f−n(v)−f−n(p)∣→0as n→∞
