to define the charecteristics of a cell, we will be using the model of a factory, as a factory needs:
- a source of energy to power its operations
- *machinery to perform various tasks*
- *exterior walls to protect its contents and regulate what enters and exits*
- *Blueprints to provide instructions for its operations*
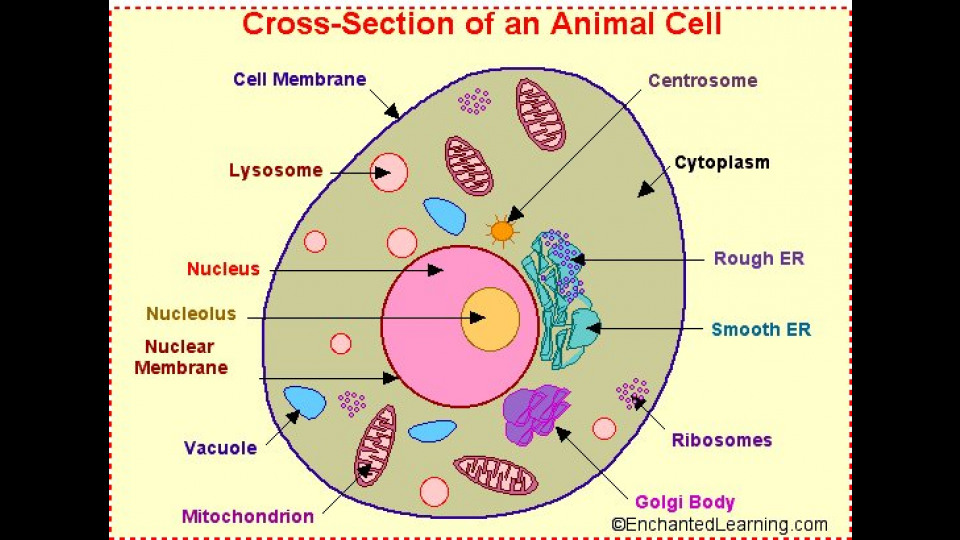
Cell Model
After definining the Atomic Cell Structure, we can finally have a look the biological result of these forces.
As an overview, a cell looks something like this:
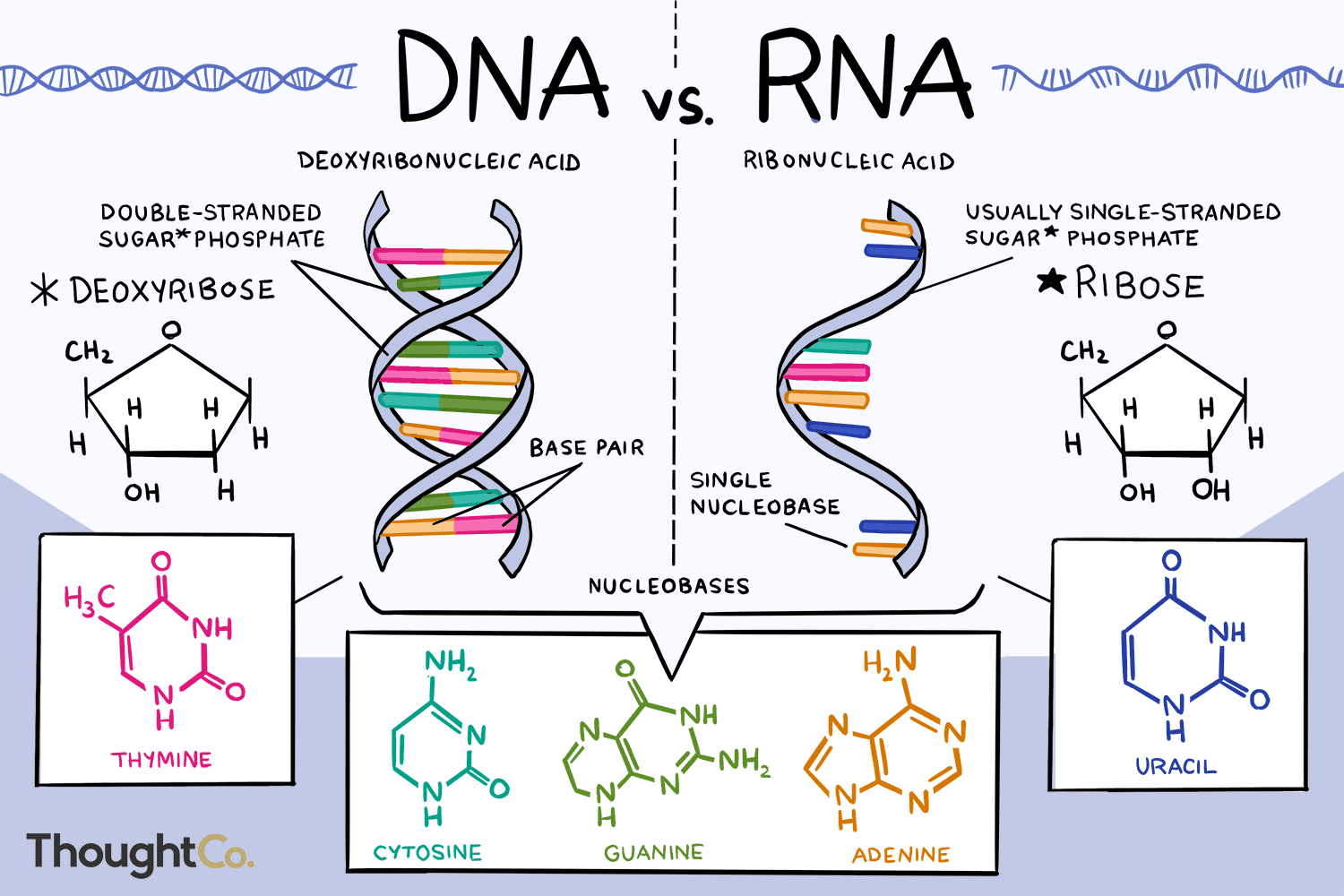
Nucleic Acids: Genetic Information
Main function is to provide intructions for the cell’s operations.
Consists of nucleotides (monomers) that make up nucleic acids (polymers).
There are two kinds of nucleic acids: DNA and RNA.
Some of these nucleotides are used to make ATP, which is the main energy currency of the cell.
DNA and RNA are chains of nucleotides connected by covalent bonds.
Proteins
Proteins are the machinery of the cell, performing a wide variety of functions. You can think of them as the doers and workers in a factory.
They speed up chemical reactions, transport molecules, provide structural support, and regulate cellular processes.
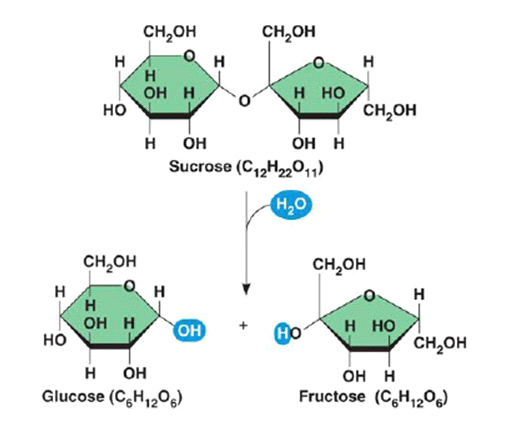
Example
Turning Sucrose into Glucose and Fructose: this reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme sucrase.
They do this with Enzymes - a type of protein that acts as a catalyst to speed up chemical reactions.
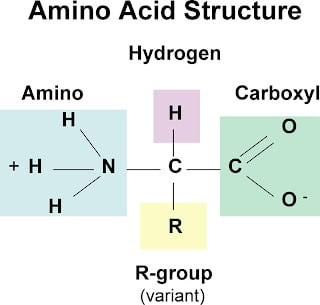
Amino Acids
Amino acids are the monomers that make up proteins (the polymers).
- set of twenty different amino acids common to ALL organisms
- share common structure
- unique side chain (R group) gives each amino acid its unique properties
Polypeptides
Chains of amino acids connected by covalent bonds are called polypeptides.
- fold inot complex structures that are essential for proper function - held together by noncovalent bonds
- shape determined by composition and order of amino acids
- a single polypeptide chain can be a functional protein, or multiple chains can come together to form a functional protein
Cell Types
Prokaryotic Cells - are simpler and smaller, lacking a nucleus and membrane-bound Organelles.
Eukaryotic Cells - are more complex, with a nucleus and various membrane-bound Organelles.