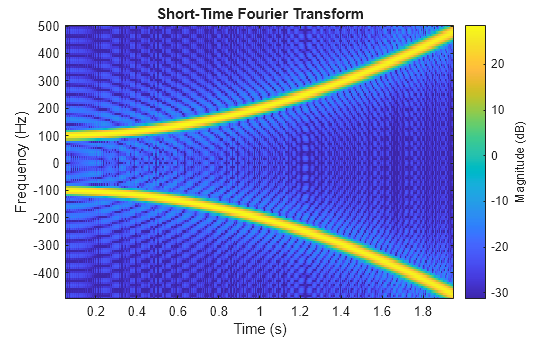
The STFT (or often STFFT) is the blend between the Fourier Transform and the concept of time windows. It allows us to analyze how the frequency content of a signal changes over time, which is particularly useful for non-stationary signals where frequency components vary.
In most practical cases, having something like a full song be converted to the frequency domain is limited in use. There are elements of the song like that notes that make proper use of frequency combinations, but in most case we take these notes to be short lived, and arranged in time. Thus, we need a way to analyze the frequency content of a signal over short time intervals.
It is formulated as:
Where:
- is a dummy variable of integration representing time.
- is the window function centered at time . This function is non-zero only over a short duration, effectively isolating a segment of the signal around time .
In plain english, we are splitting the signal into small chunks using a window function , and then applying the Fourier Transform to each chunk. The window function is typically a smooth function that tapers off at the edges, such as a Hamming or Gaussian window. We use a sliding window instead of discrete segments to avoid artifacts in the frequency analysis.