This will discuss:
- the cerebral cortex
- brain structure
- associated behavior
In Essence
Neuron: cellular building blocks of the brain
- billion neurons in the human brain
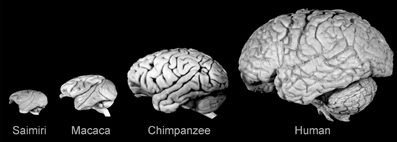
The Cerebral Cortex
The Cerebral Cortex is the outermost layer of the brain, which supports:
- cognitive skills
- complex emotions and complex mental activity
- your sense of mind and self
The most recent part of the brain from an evolutionary point of view
Do We Have Free Will?
Consider the following quote:
You, your joys and your sorrows, your memories and your ambitions, your sense of personal identity and free will, are in fact no more than the behavior of a vast assembly of nerve cells and their associated molecules.
- Francis Crick’s astonishing hypothesis
The Nervous System
[Central Nervous System]: comprised of your brain and spinal cord.
- Spinal Cord: the major conduit for information flowing to and from the brain.
- controls simple reflexes
- transmits messages between the brain and the rest of the body.
[Peripheral Nervous System]: composed of the nverves that connect the parts of your body to your brain.
- Cranial Nerves
- transmits information from your eyes, ears, nose, and mouth to the brain.
Peripheral Nervous System Sub Systems
[Sympathetic Nervous System]: acts on blood vessels, organs, and galnds in ways to prepare the body for action, especially in life threatening situations
- provides resources for the fight or flight response
- mobilizes the body to attack, defend, or flee when encountering a potential threat
- works with the Peripheral Nervous System to prepare the body for challenges
[Parasympathetic Nervous System]: returns the body to a resting state by counteracting the actions of the Sympathetic Nervous System
- performs restorative functions - “rest and digest”
- allows the body to regenerate energy when it is safe to do so
- works with the Sympathetic Nervous System to prepare the body for challenges
In Class Questions
Question
Explain what happens when you encounter a bear in the woods. What nervous systems kicks in? What does it do?
Answer
The Sympathetic Nervous System kicks in, preparing the body for a fight or flight response. It increases heart rate, dilates pupils, and redirects blood flow to muscles, enabling quick action to either confront the threat or escape from it.
Question
Why is it harmful if this nervous system is activated all the time(like in chronically stressful situations)?
Answer
The chronic activation of the Sympathetic Nervous System can lead to various health issues, including high blood pressure, weakened immune function, and increased risk of heart disease. It can also contribute to anxiety and depression due to the constant state of heightened arousal. A lack of digestion and rest can lead to fatigue and poor overall health.
Brain Worksheet
Go to 3d brain an answer the following:
| Structure | Function | Notes, such as: - origin of the name - your observations of the structure - questions you have - tips for memorizing |
|---|---|---|
| Occipital Lobe | decodes visual signals from retina via Thalamus | - origin is Latin for back of head |
| Temporal Lobe | houses memories, emotions, language comprehension. collection of Hippocampus, Primary Auditory Cortex, and Wernicke’s Area. Key for object/people/place recognition | |
| Parietal Lobe | integrates sensory information for focus prioritization, abstract coordinate system for limbs + sense of touch coordination | |
| Frontal Lobe | personality, decision making, motor control. concatonates sensory information to make decisions | |
| Corpus Callosum | connector for left and right hemispheres of cerebral cortex, primarily Axons | |
| Basal Ganglia | group for controlling voluntary movement, habitual behavors, and emotions | |
| Hippocampus | long term memory formation, communicates with rest of brain via entorhinal cortex, produces new neurons | |
| Amygdala | works with Hippocampus to create long term memory, links them with fear + agression + anxiety | |
| Thalamus | relays sensory information to rest of brain | - grand central sattion for sorting |
| Hypothalamus | ||
| Cerebellum | ||
| Brainstem, Midbrain, Medulla oblongata, Reticular Formation |