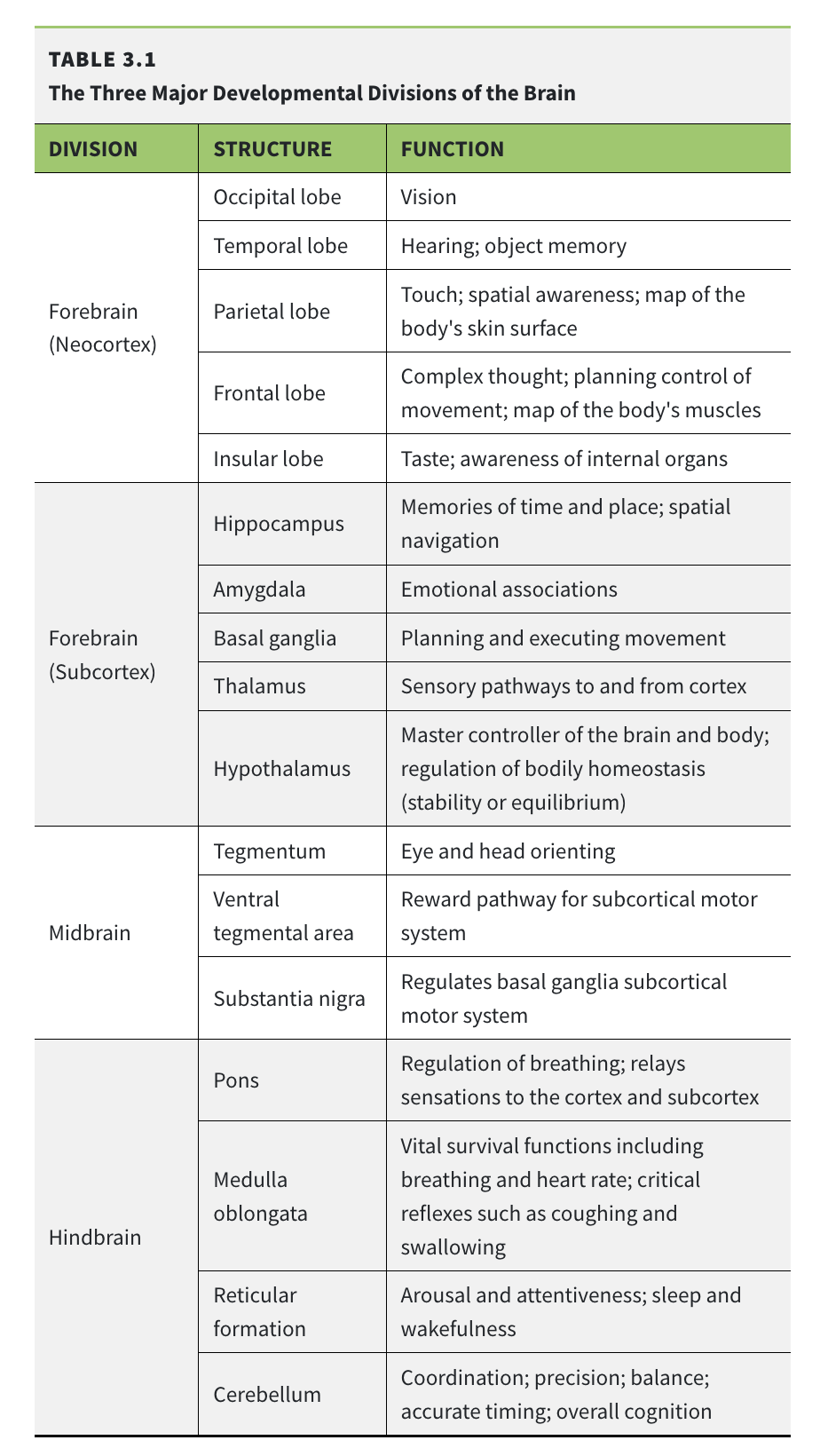
Parts of Brain
- Neocortex - Higher-order functions like thought, language, and sensory perception.
- Occipital Lobe - Processes visual information. 👀
- Temporal Lobe - Processes sounds, memory, and language comprehension. 👂
- Parietal Lobe - Integrates sensory information (touch, temperature) and spatial awareness.
- Frontal Lobe - Manages executive functions: planning, decision-making, and personality. 🧠
- Insular Lobe - Involved in emotion, self-awareness, and internal body sensations.
- Subcortex - Structures below the cortex handling memory, emotion, and drives.
- Hippocampus - Forms new memories and is key for spatial navigation. 🗺️
- Amygdala - The brain’s emotional center, especially for fear and aggression.
- Basal Ganglia - Controls voluntary motor movements, habit formation, and procedural learning.
- Thalamus - Acts as the main relay station for sensory information. 📮
- Hypothalamus - Regulates basic drives like hunger, thirst, and body temperature.
- Midbrain - Connects the forebrain and hindbrain; involved in vision, hearing, and movement.
- Tegmentum - Controls basic body and limb movements.
- Ventral tegmental area - A key part of the brain’s reward and motivation circuit (dopamine). ✨
- Substantia nigra - Important for reward and fluid movement (dopamine).
- Hindbrain - Manages vital autonomic functions for survival.
- Pons - Relays signals between the cerebrum and cerebellum; involved in sleep and facial sensation.
- Medulla oblongata - Controls involuntary functions like heartbeat and breathing. ❤️
- Reticular Formation - A network for arousal, consciousness, and the sleep-wake cycle. 😴
- Cerebellum - Coordinates fine motor control, balance, and posture. 🤸♀️
Nervous System
- Central Nervous System (CNS)
- Comprises the brain and spinal cord
- Controls voluntary movements, thoughts, emotions, and other bodily functions
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- Extends from the CNS to the rest of the body
- Includes:
- Somatic Nervous System: Controls voluntary movements, such as muscle contractions
- Autonomic Nervous System: Regulates involuntary bodily functions, such as heart rate, digestion, and sweating
- The autonomic nervous system is further divided into:
- Sympathetic Nervous System: Activates the “fight or flight” response
- Parasympathetic Nervous System: Calms the body down after a stressful situation
More Brain
- Dorsal Pathway - where and how to interact with
- Ventral Pathway - what an object is
Imaging
- Event-related potential (ERP)
- Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Functional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Positron emission tomography (PET)