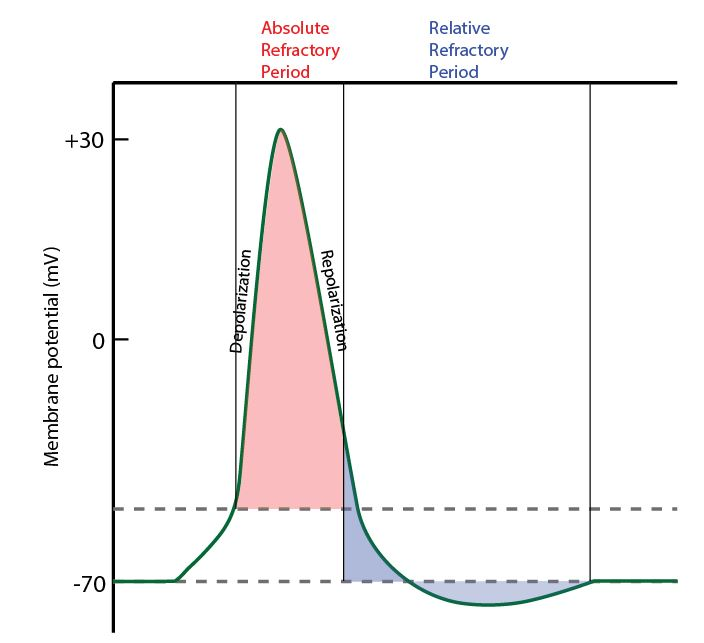
The refractory period is the temporary state a Neuron is in after an Action potential. During this period, the cell cannot respond to any further stimuli, regardless of their intensity.
There are two phases of the refractory period:
- Absolute refractory period: During this phase, the neuron is completely incapable of firing another action potential. This is due to the inactivation of sodium channels that were opened during the action potential.
- Relative refractory period: In this phase, the neuron can fire another action potential, but it is more difficult than usual. This is because some sodium channels have returned to their resting state, but the neuron is still hyperpolarized due to the continued efflux of potassium ions.