The Laplace distribution, also known as the double exponential distribution, is a continuous probability distribution named after Pierre-Simon Laplace. It is characterized by its sharp peak at the mean and heavier tails compared to the normal distribution.
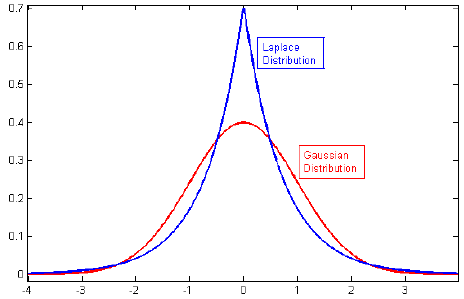
This distribution is exceptionally useful in real world phenomena in which data exhibits a higher likelihood of extreme values, such as in finance for modeling asset returns, in signal processing for noise reduction, and in various fields of engineering and environmental science. Oftentimes, there is a bias towards 0 or the mean, but with occasional large deviations.
It is characterized by the equation: