- Psychology as a science
- Understanding Cognitive Bias
- Scientifically Understanding Human Behavior
Limits of Intuition and Experience
People use different strategies for understanding human behavior:
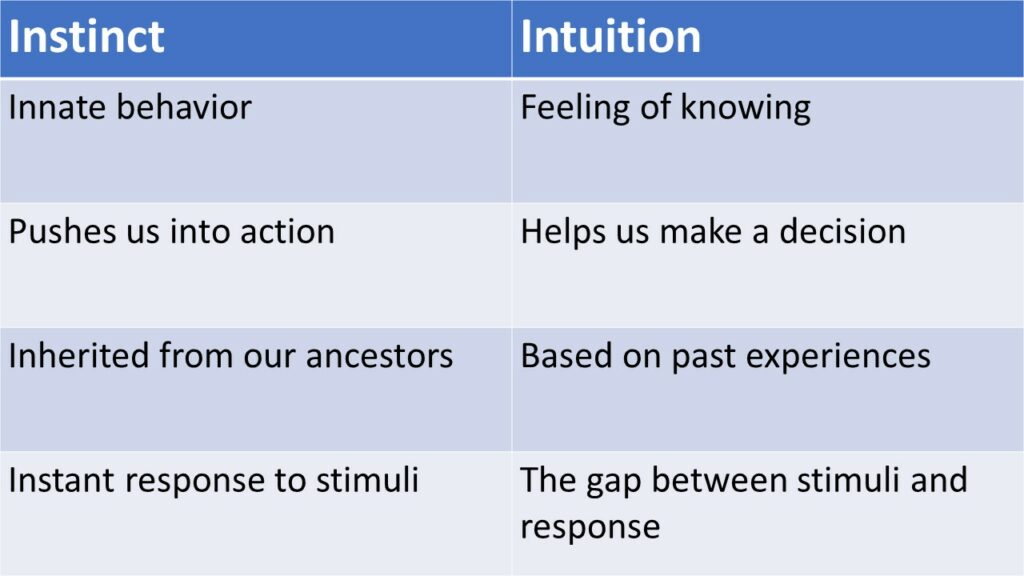
- Experience: personal events relating to the phenomenon
- Intuition: subjective feelings about what makes sense
Whats Wrong with Intuition and Experience?
- We experience only one version of each situation
- Even when we notice patterns, there may be multiple explanations
- Confidence in our intuitions does not mean they are correct
What even is Psychology?
In Laymann’s terms, Psychology is the scientific study of the mind and its associated behavior.
It is relevant to all aspects of human experience, and it helps us solve problems individually and societally.
But how is it a science, and not instead a philosophy?
Psychology IS a Science
Psychological sciences work by the use of rigorous scientific methods to develop insights into the human mind and human behavior.
The science of psychology overcomes biased conclusions and narrow experiences.
How Do I Think like a Psychological Scientist?
There are two main principles behind thinking like a scientist in the domain of Psychology:
- Critical: curious, skeptical, and open-minded
- Summative: use evidence to support claims
Biases Preventing This
Biases are systematic errors in thinking that affect the decisions and judgments that people make. This is partly why it is so hard to think like a psychology scientist.
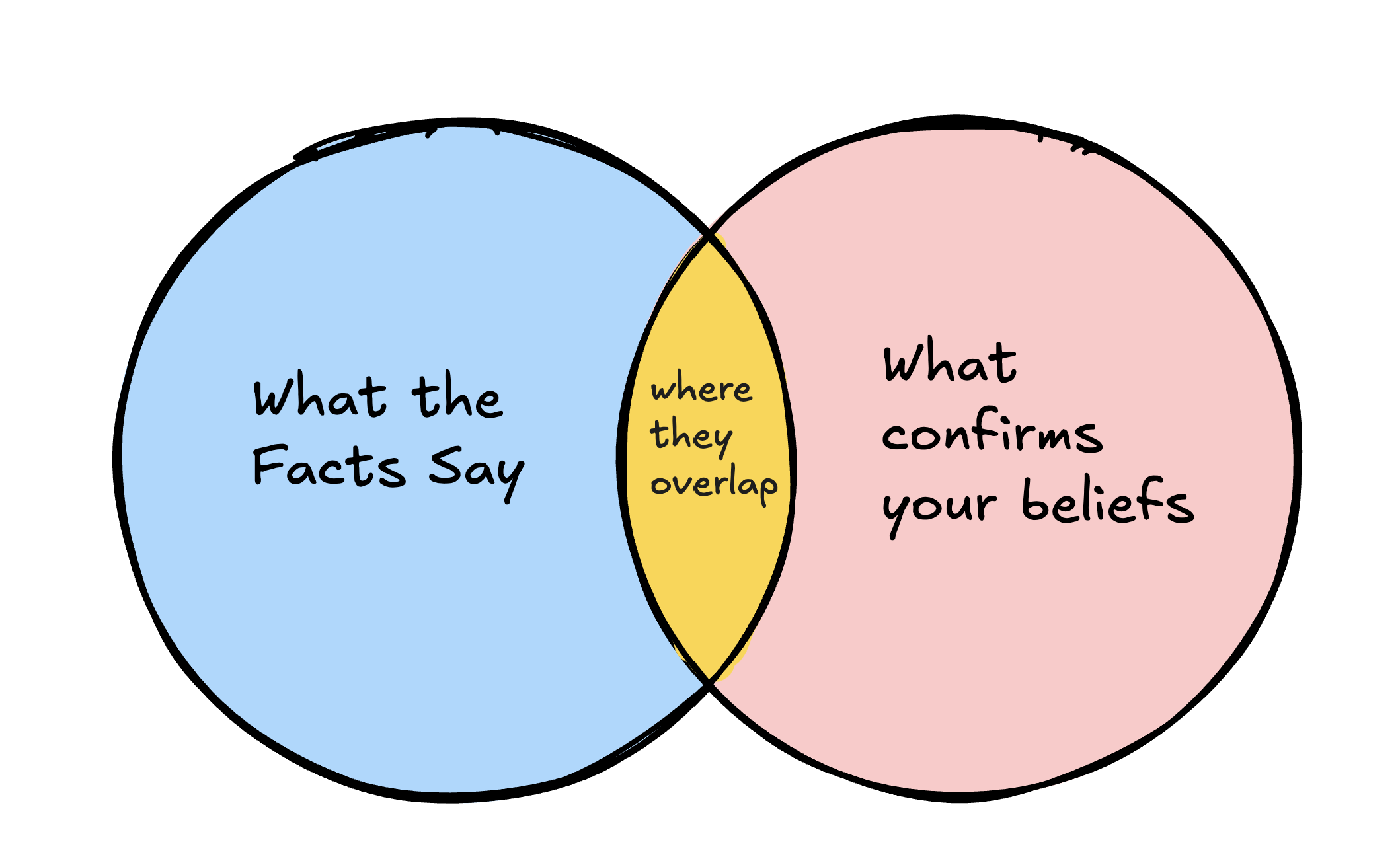
Confirmation Bias
Confirmation bias is simply defined as the tendancy for people to favor information that confirms their preexisting beliefs or hypotheses.
Overconfidence Bias
This is the tendency to be more confident than correct - to overestimate the accuracy of our beliefs and judgments.
A perfect example of this is the Titanic, where the ship was said to be “unsinkable”, and the crew were overconfident in their ability to handle any situation.

How Do We Overcome These Challenges?
Critical Thinking is the scientific attitude that psychologists use to overcome these biases.
Some key questions to ask when evaluating claims:
- what is the source of the claim?
- has the claim been verified?
- is this an opinion piece or a scientific study?